Plotting with seaborn
ScmData provides limited support for plotting. However, we make it as easy as possible to return data in a format which can be used with the seaborn plotting library. Given the power of this library, we recommend having a look through its documentation if you want to make anything more than the most basic plots.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from scmdata.plotting import RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS
from scmdata.run import ScmRun
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/scmdata/checkouts/stable/src/scmdata/database/_database.py:9: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
import tqdm.autonotebook as tqdman
Data
For this notebook we use the RCMIP radiative forcings, available at rcmip.org.
rcmip_db = ScmRun("rcmip-radiative-forcing-annual-means-v4-0-0.csv")
rcmip_db.head()
| time | 1750-01-01 00:00:00 | 1751-01-01 00:00:00 | 1752-01-01 00:00:00 | 1753-01-01 00:00:00 | 1754-01-01 00:00:00 | 1755-01-01 00:00:00 | 1756-01-01 00:00:00 | 1757-01-01 00:00:00 | 1758-01-01 00:00:00 | 1759-01-01 00:00:00 | ... | 2491-01-01 00:00:00 | 2492-01-01 00:00:00 | 2493-01-01 00:00:00 | 2494-01-01 00:00:00 | 2495-01-01 00:00:00 | 2496-01-01 00:00:00 | 2497-01-01 00:00:00 | 2498-01-01 00:00:00 | 2499-01-01 00:00:00 | 2500-01-01 00:00:00 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| activity_id | mip_era | model | region | scenario | unit | variable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| not_applicable | CMIP5 | AIM | World | rcp60 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 |
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols|Aerosols-cloud Interactions | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols|Aerosols-radiation Interactions | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 |
5 rows × 751 columns
Plotting with ScmRun
For the most common plotting patterns, we provide a very simple lineplot method in ScmRun.
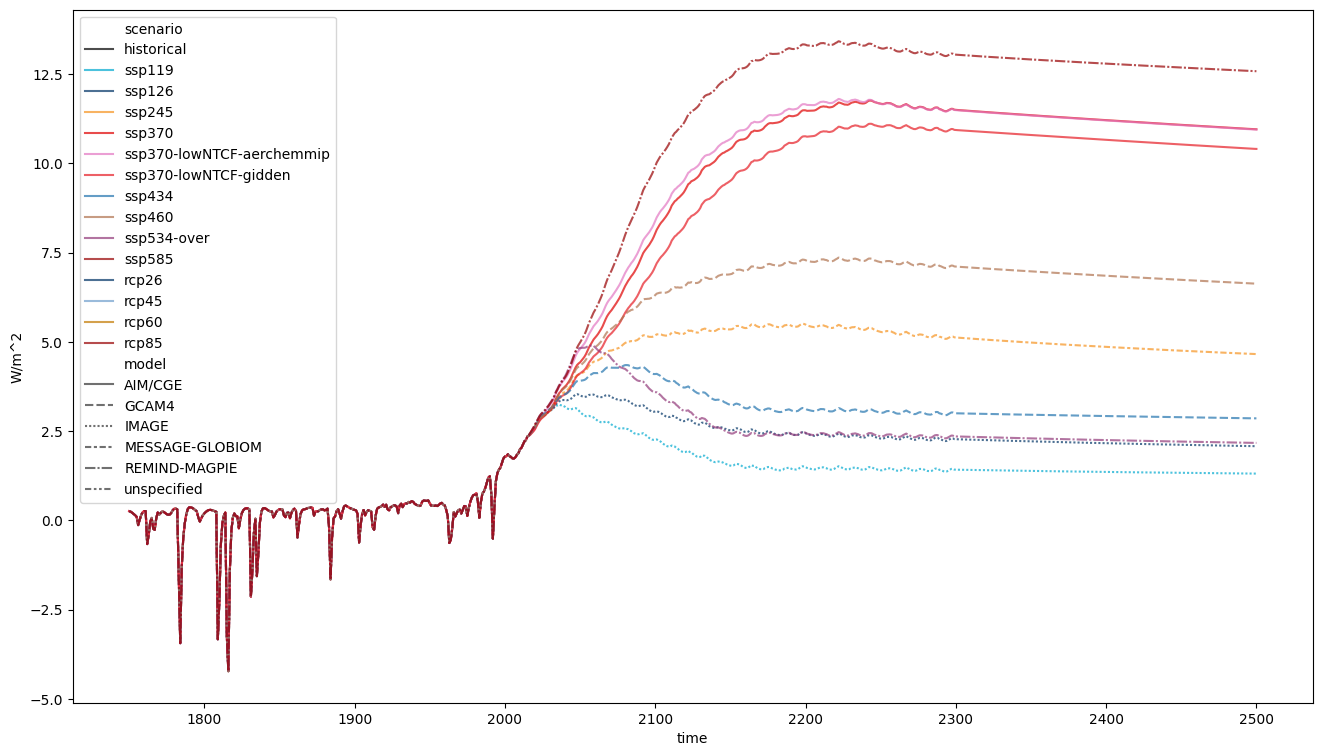
out = rcmip_db.filter(variable="Effective Radiative Forcing").lineplot()
out
<Axes: xlabel='time', ylabel='W/m^2'>
kwargs passed to this method are given directly to
seaborn.lineplot,
which allows an extra layer of control.
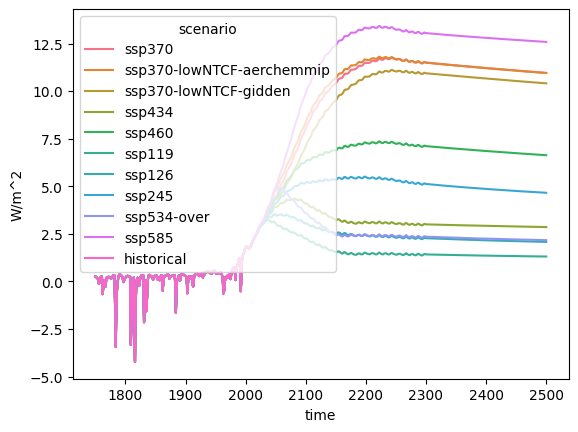
For example, we can plot on slightly bigger axes, make the lines slightly transparent, add markers for the different models, specify the colour to use for each scenario and specify the order to display the scenarios in.
ax = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 9)).add_subplot(111)
rcmip_db.filter(variable="Effective Radiative Forcing").lineplot(
ax=ax,
hue="scenario",
palette=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS,
hue_order=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS.keys(),
style="model",
alpha=0.7,
)
<Axes: xlabel='time', ylabel='W/m^2'>
Specifying the time axis
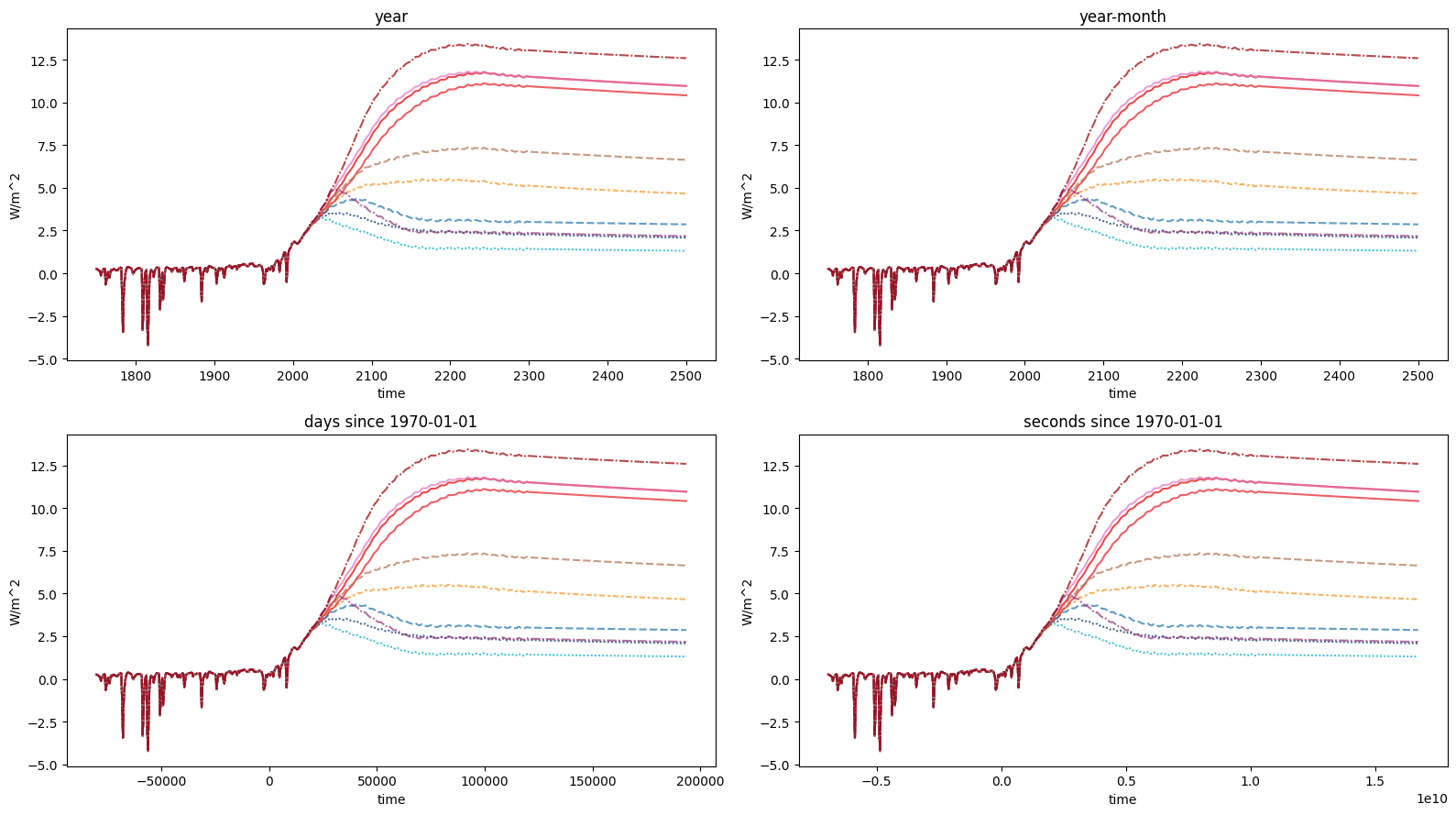
Plotting with a datetime.datetime time axis is not always convenient.
To address this, we provide the time_axis keyword argument. The options are available in the
lineplot docstring.
print(rcmip_db.lineplot.__doc__)
Make a line plot via `seaborn's lineplot
See seaborn documentation for a complete description of the kwargs
<https://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.lineplot.html>`_
If only a single unit is present, it will be used as the y-axis label.
The axis object is returned so this can be changed by the user if desired.
Parameters
----------
time_axis : {None, "year", "year-month", "days since 1970-01-01", "seconds since 1970-01-01"}
Time axis to use for the plot.
If ``None``, :class:`datetime.datetime` objects will be used.
If ``"year"``, the year of each time point will be used.
If ``"year-month"``, the year plus (month - 0.5) / 12 will be used.
If ``"days since 1970-01-01"``, the number of days since 1st Jan 1970 will be
used (calculated using the :mod:`datetime` module).
If ``"seconds since 1970-01-01"``, the number of seconds since 1st Jan 1970 will
be used (calculated using the :mod:`datetime` module).
**kwargs
Keyword arguments to be passed to ``seaborn.lineplot``. If none are passed,
sensible defaults will be used.
Returns
-------
:class:`matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot`
Output of call to ``seaborn.lineplot``
fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 9), nrows=2, ncols=2)
pdb = rcmip_db.filter(variable="Effective Radiative Forcing")
for ax, time_axis in zip(
axes.flatten(),
[
"year",
"year-month",
"days since 1970-01-01",
"seconds since 1970-01-01",
],
):
pdb.lineplot(
ax=ax,
hue="scenario",
palette=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS,
hue_order=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS.keys(),
style="model",
alpha=0.7,
time_axis=time_axis,
legend=False,
)
ax.set_title(time_axis)
plt.tight_layout()
These same options can also be passed to the timeseries and long_data methods.
rcmip_db.timeseries(time_axis="year-month")
| time | 1750.041667 | 1751.041667 | 1752.041667 | 1753.041667 | 1754.041667 | 1755.041667 | 1756.041667 | 1757.041667 | 1758.041667 | 1759.041667 | ... | 2491.041667 | 2492.041667 | 2493.041667 | 2494.041667 | 2495.041667 | 2496.041667 | 2497.041667 | 2498.041667 | 2499.041667 | 2500.041667 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| activity_id | mip_era | model | region | scenario | unit | variable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| not_applicable | CMIP5 | AIM | World | rcp60 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 | 5.993838 |
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | 5.890082 | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | -0.603691 | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols|Aerosols-cloud Interactions | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | -0.465404 | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols|Aerosols-radiation Interactions | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | -0.138286 | ||||||
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ||
| unspecified | World | historical-cmip5 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Stratospheric Ozone | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ||
| Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Tropospheric Ozone | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Natural | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Natural|Solar | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ||||||
| Radiative Forcing|Natural|Volcanic | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
499 rows × 751 columns
rcmip_db.long_data(time_axis="days since 1970-01-01")
| activity_id | mip_era | model | region | scenario | unit | variable | time | value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | AIM | World | rcp60 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing | -74874 | 0.000000 |
| 1 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | AIM | World | rcp60 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing | -74509 | 0.126027 |
| 2 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | AIM | World | rcp60 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing | -74144 | 0.273031 |
| 3 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | AIM | World | rcp60 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing | -73779 | 0.278871 |
| 4 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | AIM | World | rcp60 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing | -73413 | 0.242045 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 332450 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | unspecified | World | historical-cmip5 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing|Natural|Volcanic | 11323 | 0.232444 |
| 332451 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | unspecified | World | historical-cmip5 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing|Natural|Volcanic | 11688 | 0.232444 |
| 332452 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | unspecified | World | historical-cmip5 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing|Natural|Volcanic | 12053 | 0.232444 |
| 332453 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | unspecified | World | historical-cmip5 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing|Natural|Volcanic | 12418 | 0.232444 |
| 332454 | not_applicable | CMIP5 | unspecified | World | historical-cmip5 | W/m^2 | Radiative Forcing|Natural|Volcanic | 12784 | 0.184018 |
332455 rows × 9 columns
Plotting with seaborn
If you wish to make plots which are more complex than this most basic pattern, a combination of seaborn and pandas reshaping is your best bet.
Plotting on a grid
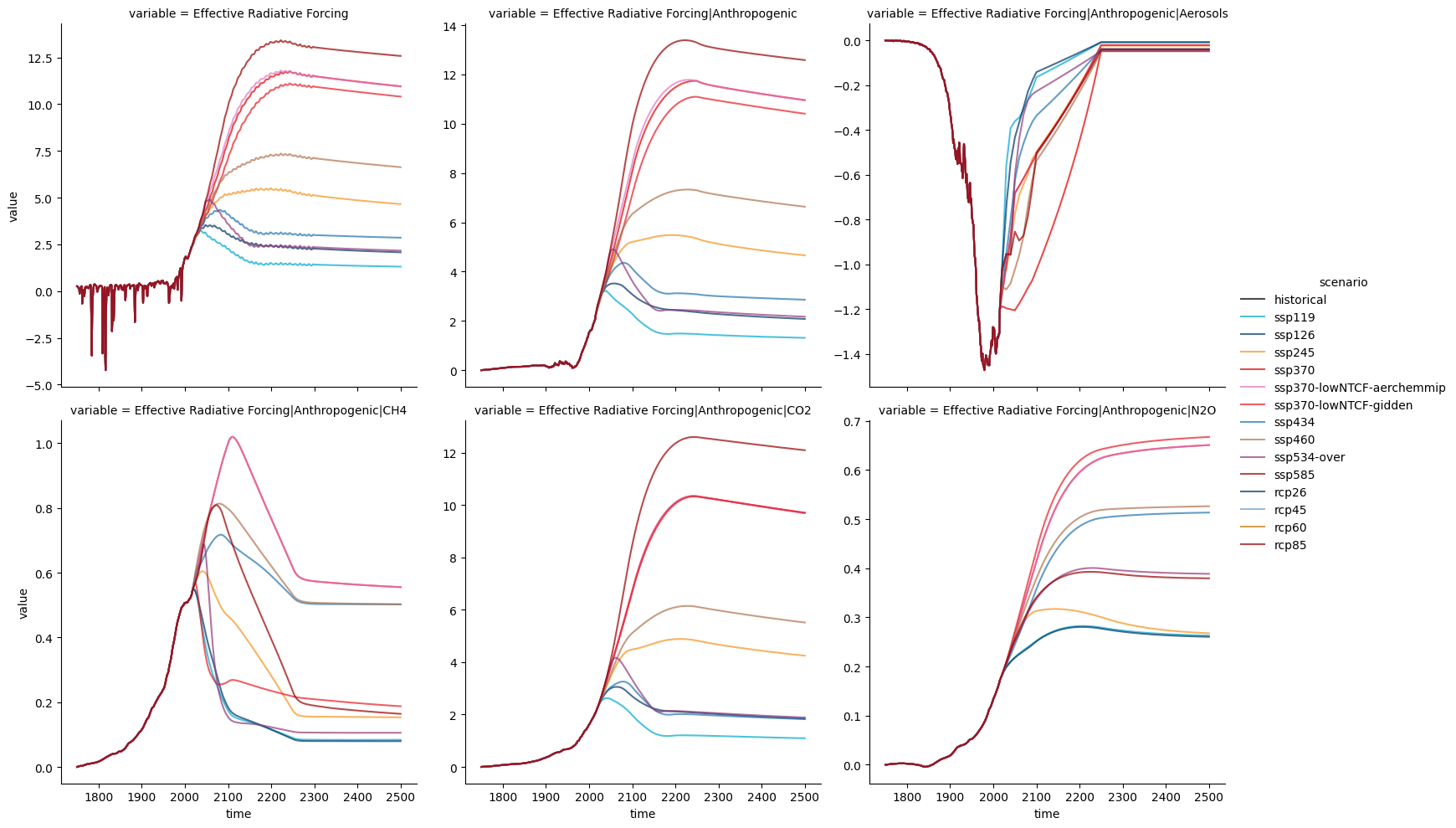
Often we wish to look at lots of different variables at once. Seaborn allows this sort of ‘gridded’ plotting, as shown below.
vars_to_plot = ["Effective Radiative Forcing"] + [
f"Effective Radiative Forcing|{v}"
for v in [
"Anthropogenic",
"Anthropogenic|Aerosols",
"Anthropogenic|CO2",
"Anthropogenic|CH4",
"Anthropogenic|N2O",
]
]
vars_to_plot
['Effective Radiative Forcing',
'Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic',
'Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols',
'Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|CO2',
'Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|CH4',
'Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|N2O']
seaborn_df = rcmip_db.filter(variable=vars_to_plot).long_data()
seaborn_df.head()
| activity_id | mip_era | model | region | scenario | unit | variable | time | value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | Effective Radiative Forcing | 1750-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.259367 |
| 1 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | Effective Radiative Forcing | 1751-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.242788 |
| 2 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | Effective Radiative Forcing | 1752-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.214656 |
| 3 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | Effective Radiative Forcing | 1753-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.179488 |
| 4 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | Effective Radiative Forcing | 1754-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.145354 |
With the output of .long_data() we can directly use
seaborn.relplot.
sns.relplot(
data=seaborn_df,
x="time",
y="value",
col="variable",
col_wrap=3,
hue="scenario",
palette=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS,
hue_order=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS.keys(),
alpha=0.7,
facet_kws={"sharey": False},
kind="line",
)
<seaborn.axisgrid.FacetGrid at 0x7fc693c42ca0>
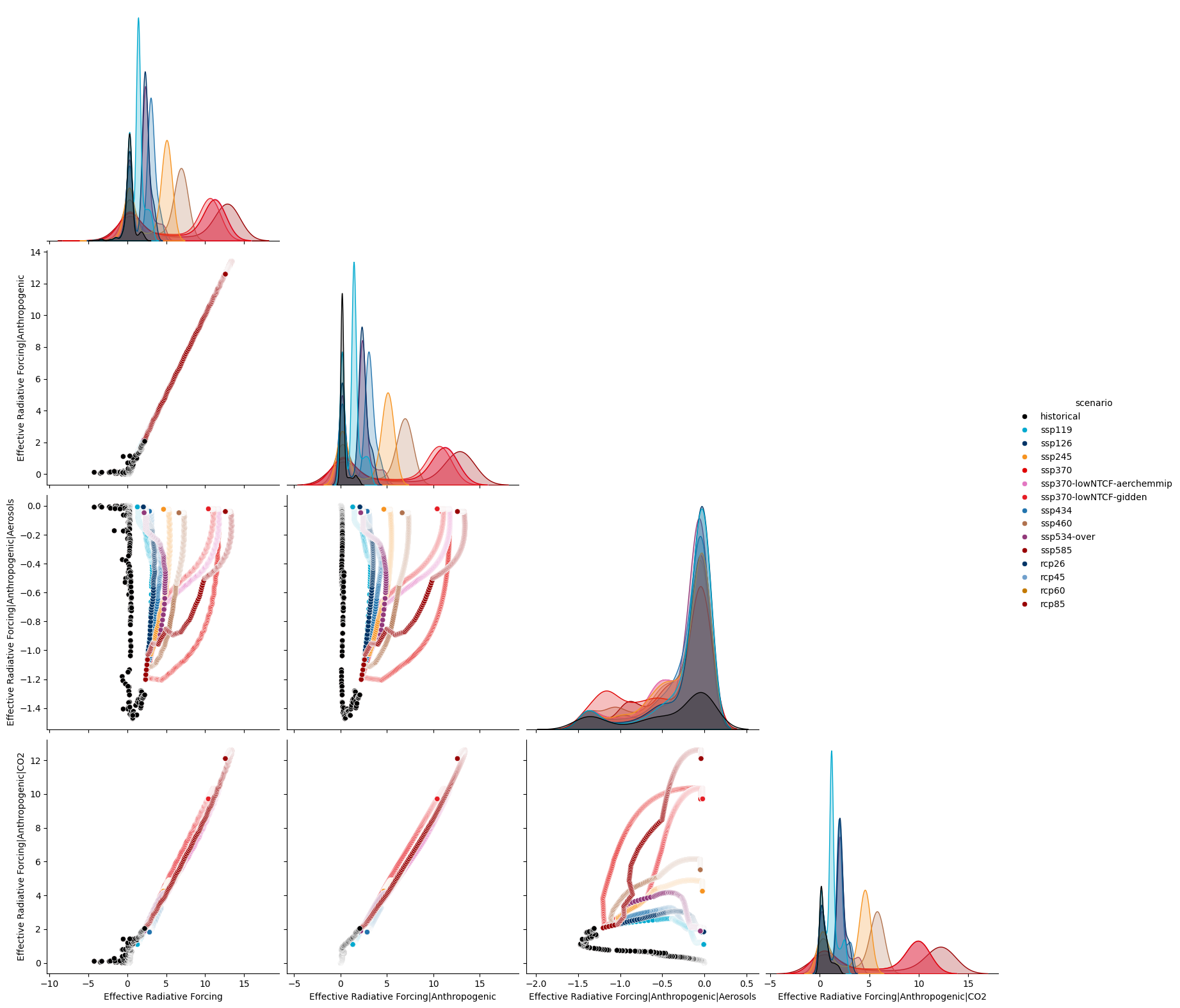
Variable scatter plots
Sometimes we don’t want to plot against time, rather we want to plot variables against each other. For example, we might want to see how the effective radiative forcings relate to each other in the different scenarios. In such a case we can reshape the data using pandas before using seaborn.
ts = rcmip_db.filter(variable=vars_to_plot[:4]).timeseries()
ts.head()
| time | 1750-01-01 00:00:00 | 1751-01-01 00:00:00 | 1752-01-01 00:00:00 | 1753-01-01 00:00:00 | 1754-01-01 00:00:00 | 1755-01-01 00:00:00 | 1756-01-01 00:00:00 | 1757-01-01 00:00:00 | 1758-01-01 00:00:00 | 1759-01-01 00:00:00 | ... | 2491-01-01 00:00:00 | 2492-01-01 00:00:00 | 2493-01-01 00:00:00 | 2494-01-01 00:00:00 | 2495-01-01 00:00:00 | 2496-01-01 00:00:00 | 2497-01-01 00:00:00 | 2498-01-01 00:00:00 | 2499-01-01 00:00:00 | 2500-01-01 00:00:00 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| activity_id | mip_era | model | region | scenario | unit | variable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | Effective Radiative Forcing | 0.259367 | 0.242788 | 0.214656 | 0.179488 | 0.145354 | 0.098651 | -0.133032 | 0.016012 | 0.147192 | 0.226591 | ... | 10.978680 | 10.976215 | 10.973747 | 10.971275 | 10.968806 | 10.966383 | 10.963918 | 10.961447 | 10.959022 | 10.957785 |
| Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic | 0.000000 | 0.001756 | 0.003698 | 0.004707 | 0.004987 | 0.007033 | 0.008562 | 0.008844 | 0.010441 | 0.011487 | ... | 10.978680 | 10.976215 | 10.973747 | 10.971275 | 10.968806 | 10.966383 | 10.963918 | 10.961447 | 10.959022 | 10.957785 | ||||||
| Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols | 0.000000 | 0.000836 | 0.001212 | 0.000801 | -0.000571 | 0.000063 | 0.000618 | -0.001421 | -0.000764 | -0.000720 | ... | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | -0.043755 | ||||||
| Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|CO2 | 0.000000 | 0.000824 | 0.001647 | 0.002330 | 0.003153 | 0.004097 | 0.004859 | 0.005923 | 0.006866 | 0.007890 | ... | 9.719260 | 9.716890 | 9.714518 | 9.712146 | 9.709772 | 9.707446 | 9.705070 | 9.702694 | 9.700365 | 9.699176 | ||||||
| ssp370-lowNTCF-aerchemmip | W/m^2 | Effective Radiative Forcing | 0.259367 | 0.242788 | 0.214656 | 0.179488 | 0.145354 | 0.098651 | -0.133032 | 0.016012 | 0.147192 | 0.226591 | ... | 10.969436 | 10.966971 | 10.964503 | 10.962031 | 10.959561 | 10.957139 | 10.954674 | 10.952202 | 10.949777 | 10.948541 |
5 rows × 751 columns
ts_reshaped = ts.unstack("variable").stack("time").reset_index()
ts_reshaped.head()
/tmp/ipykernel_809/4198992639.py:1: FutureWarning: The previous implementation of stack is deprecated and will be removed in a future version of pandas. See the What's New notes for pandas 2.1.0 for details. Specify future_stack=True to adopt the new implementation and silence this warning.
ts_reshaped = ts.unstack("variable").stack("time").reset_index()
| variable | activity_id | mip_era | model | region | scenario | unit | time | Effective Radiative Forcing | Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic | Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|Aerosols | Effective Radiative Forcing|Anthropogenic|CO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | 1750-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.259367 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 1 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | 1751-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.242788 | 0.001756 | 0.000836 | 0.000824 |
| 2 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | 1752-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.214656 | 0.003698 | 0.001212 | 0.001647 |
| 3 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | 1753-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.179488 | 0.004707 | 0.000801 | 0.002330 |
| 4 | not_applicable | CMIP6 | AIM/CGE | World | ssp370 | W/m^2 | 1754-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.145354 | 0.004987 | -0.000571 | 0.003153 |
sns.pairplot(
ts_reshaped,
hue="scenario",
palette=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS,
hue_order=RCMIP_SCENARIO_COLOURS.keys(),
corner=True,
height=4,
)
<seaborn.axisgrid.PairGrid at 0x7fc692d7eee0>